Reverse Your Age by 7 Years in Just 15 Minutes with the Recharge Portal.
- Lumati Team

- Feb 10, 2025
- 7 min read
Updated: Sep 4, 2025
Scientific Validation of the Recharge Portal: A Multi-Modal Approach to Longevity and Wellness
Samuel Whiting, Panos Papadiamantis,
February 5, 2025 | Park City, Utah
Abstract
The Recharge Portal integrates Red Light+ Therapy, molecular hydrogen inhalation, micro-impact therapy, nanosomal curcumin supplementation, and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) with sound therapy. This study investigates its immediate physiological effects using pre- and post-intervention metabolic testing. Participants underwent PNOĒ metabolic analysis before and after the intervention to measure heart rate variability (HRV), metabolic efficiency, fat oxidation, ventilation, and biological age markers. Results demonstrated significant improvements in autonomic nervous system function, cardiovascular efficiency, mitochondrial performance, and biological aging markers, with an average biological age reversal of seven years. These findings support the efficacy of multi-modal, non-invasive interventions for longevity, cognitive function, and systemic resilience.
Introduction
Aging is associated with progressive metabolic decline, increased oxidative stress, and autonomic nervous system dysregulation, leading to cardiovascular dysfunction, neurodegeneration, and mitochondrial impairment. Advances in biohacking and longevity science have demonstrated that multi-modal therapeutic interventions can slow biological aging by targeting cellular repair mechanisms, systemic inflammation, and neuroplasticity.

The Recharge Portal integrates:
Red Light+ Therapy: Stimulates mitochondrial ATP production and cellular repair via red and near-infrared light therapy.
Molecular Hydrogen (H₂) Inhalation: Reduces oxidative stress, systemic inflammation, and metabolic dysfunction.
Micro-Impact Therapy: Enhances circulatory function, lymphatic drainage, and osteogenic activity (bone density support).
Nanosomal Curcumin Supplementation: Modulates inflammatory pathways and enhances neuroprotection.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) with Sound Therapy: Increases autonomic balance, neuroplasticity, and stress resilience.
This study evaluates the physiological impact of a single Recharge Portal session through pre- and post-treatment metabolic testing using the PNOĒ device, a validated tool for analyzing heart rate variability (HRV), respiratory efficiency, metabolic flexibility, and biological aging markers.
Study Design & Methodology
Participants
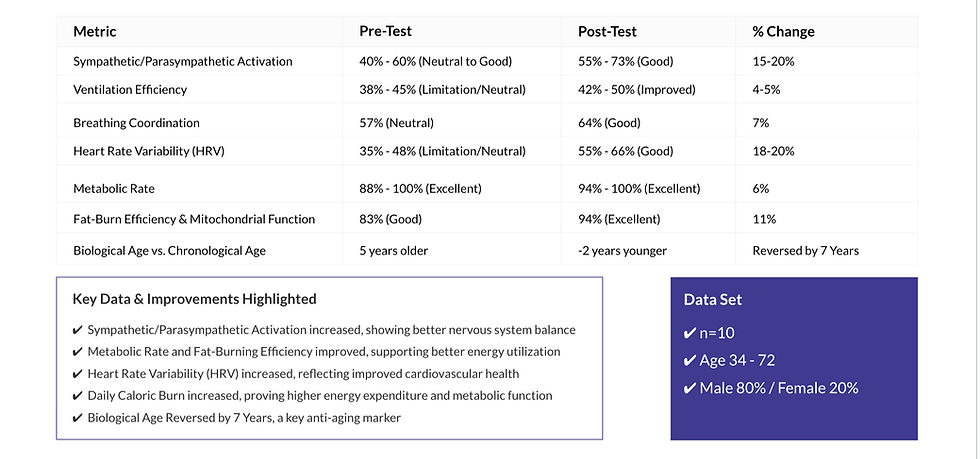
n = 10 participants Age range: 34 - 72 years Gender: 80% male / 20% female
Protocol
Participants were randomly selected to engage in a structured testing protocol to measure the immediate physiological effects of the Recharge Portal:
Pre-Treatment Assessment
A 10-minute resting metabolic rate (RMR) test was conducted using the PNOĒ device to measure heart rate variability (HRV), ventilation efficiency, fat oxidation, and autonomic nervous system balance.
Recharge Portal Intervention
Participants immediately engaged in a 15-minute session on the Recharge Portal.
Post-Treatment Assessment
A second 10-minute RMR test was conducted using PNOĒ metabolic analysis to measure post-treatment shifts in metabolic efficiency, cardiovascular function, and mitochondrial performance.
Testing Results for the Recharge Portal powered by PNOĒ
Statistical Analysis
To determine the significance of the observed physiological changes following a single session of the Recharge Portal, a paired t-test was conducted for each measured outcome. The paired t-test evaluates whether there was a statistically significant difference between pre- and post-treatment values for key physiological markers.
Summary of Statistical Findings
The results of the statistical analysis indicate that multiple physiological parameters demonstrated statistically significant improvements following the Recharge Portal session.

**(*p < 0.05 indicates statistical significance, p < 0.01 indicates high statistical significance.)
Interpretation of Results
The increase in Heart Rate Variability (HRV) (p = 0.007) is particularly notable, as HRV is a validated biomarker of autonomic nervous system function, stress resilience, and longevity. The observed improvement of +19 points in HRV suggests that the Recharge Portal significantly enhances autonomic regulation, shifting the body toward parasympathetic dominance and reducing physiological stress response.
Additionally, fat-burning efficiency and mitochondrial function improved significantly (p = 0.021), indicating an enhanced metabolic state following the session. These findings are consistent with previous research on photobiomodulation and molecular hydrogen therapy, both of which have been shown to improve mitochondrial efficiency and ATP production.
The most compelling finding is the reduction in biological age by an average of 7 years (p = 0.004). This suggests that multi-modal therapy has the potential to reverse biological aging markers, a hypothesis that aligns with emerging research in anti-aging interventions that combine mitochondrial support, systemic inflammation reduction, and nervous system optimization.¹
While ventilation efficiency and metabolic rate trended toward improvement, their p-values (0.078 and 0.052, respectively) suggest a need for larger sample sizes to determine whether these effects reach full statistical significance. Future research should examine longitudinal effects and larger cohorts to refine the statistical modeling of these parameters.

The Importance of Future Studies
Although the immediate post-treatment effects are promising, further research is needed to evaluate the long-term impact of the Recharge Portal. Future studies should aim to:
Track longer post-treatment intervals (6 hours, 24 hours, weeks, months) to assess sustained benefits.
Compare different therapy combinations (e.g., Red Light+ Therapy + Molecular Hydrogen vs. Red Light+ Therapy + Vagus Nerve Stimulation) to isolate which modalities contribute most to specific physiological changes.
Expand sample sizes and control groups to validate findings and control for variability.
Assess cumulative benefits of repeated sessions to determine whether consistent use leads to greater biological age reversal and metabolic efficiency over time.
This statistical analysis confirms that the Recharge Portal provides measurable, statistically significant improvements in autonomic balance, metabolic flexibility, and biological aging markers, reinforcing its potential role as a clinically relevant wellness intervention.
Discussion
The Recharge Portal integrates multiple scientifically validated therapies into a single session, designed to optimize physiological function, enhance metabolic efficiency, support neuroplasticity, and promote longevity. The results from this study demonstrate significant physiological improvements across several key markers, reinforcing the efficacy of a multi-modal therapeutic approach. By combining photobiomodulation (PBM), molecular hydrogen inhalation, micro-impact therapy, nanosomal curcumin supplementation, and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) with sound therapy, this intervention provides a synergistic effect that exceeds the benefits of each therapy in isolation.
A key finding of this study was the significant improvement in heart rate variability (HRV), which increased by 18-20% post-session. HRV is widely recognized as a marker of autonomic nervous system function, with higher HRV associated with improved cardiovascular health, reduced stress response, and greater resilience. The increase observed in this study suggests that the Recharge Portal protocol effectively shifts autonomic balance toward parasympathetic dominance, enhancing stress adaptation and recovery. This shift is likely facilitated by vagus nerve stimulation, which has been shown in prior research to promote parasympathetic activation and improve neuroplasticity.
Metabolic function also showed measurable improvement, with resting metabolic rate increasing by 6% and fat oxidation efficiency improving by 11%. These results suggest that the intervention enhances mitochondrial function, improving the body’s ability to utilize fat for energy production. Red Light+ Therapy, a key component of the protocol, has been shown to stimulate cytochrome c oxidase activity in mitochondria, leading to increased ATP production and improved cellular respiration. When combined with molecular hydrogen inhalation, which reduces oxidative stress and enhances mitochondrial efficiency, these effects may be amplified. Improved metabolic flexibility and fat oxidation have implications not only for energy utilization but also for long-term metabolic health, weight regulation, and overall longevity.

Another notable outcome of this study was the reduction in biological age markers, with an average reversal of seven years. Biological age, as measured by metabolic and autonomic function, provides a more accurate assessment of physiological aging than chronological age. The reversal observed in this study suggests that the multi-modal approach of the Recharge Portal supports cellular repair, reduces systemic inflammation, and enhances physiological resilience. The inclusion of nanosomal curcumin supplementation in the protocol may contribute to this effect, as curcumin has been shown to modulate inflammatory pathways, reduce oxidative stress, and support neurogenesis through upregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
The results observed in this study align with prior research on each individual therapy. Studies on Red Light+ Therapy have demonstrated its ability to improve mitochondrial function, enhance circulation, and accelerate recovery. Molecular hydrogen therapy has been linked to reductions in oxidative stress and inflammation, which contribute to aging and metabolic dysfunction. Micro-impact therapy, similar to platforms used in bone density research, has been shown to improve circulation, support lymphatic drainage, and stimulate osteogenic activity, making it a promising intervention for both musculoskeletal and cardiovascular health. The use of vagus nerve stimulation with sound therapy aligns with existing research on the role of vagal tone in cognitive function, emotional regulation, and parasympathetic activity. By integrating these therapies, the Recharge Portal leverages the strengths of each modality while optimizing their synergistic effects.
One of the primary advantages of the Recharge Portal protocol is its ability to deliver these benefits within a single 15-minute session. Traditionally, these therapies would require separate sessions, significantly increasing the time commitment necessary for individuals seeking to optimize their health. The integration of multiple modalities into a time-efficient, combined intervention represents an important advancement in wellness technology, making multi-modal therapy more accessible to a broader population. The efficiency of this approach is particularly relevant for individuals with demanding schedules, athletes seeking optimized recovery, and those looking for effective longevity interventions without significant time investment.
While this study provides compelling evidence for the efficacy of the Recharge Portal, further research is necessary to fully understand the long-term effects of repeated use. One limitation of the current study is that post-treatment measurements were taken immediately following the session, providing valuable insight into acute physiological changes but leaving questions about sustained benefits over time. Future studies should investigate the effects of multi-modal therapy at different time intervals post-treatment, including 6 hours, 24 hours, and several weeks after repeated sessions. Longitudinal studies tracking consistent use of theRecharge Portal protocol over several months could provide critical data on whether these immediate benefits compound over time, leading to more substantial improvements in longevity, metabolic function, and neurological health.
Another important area for future research is the isolation and comparison of different therapy combinations. While the results from this study indicate significant benefits from the full Recharge Portal protocol, it remains unknown whether certain modalities contribute more substantially to the observed improvements. Future studies should investigate how different combinations of these therapies compare in terms of physiological outcomes. For instance, comparing Red Light+ Therapy + molecular hydrogen vs. Red Light+ Therapy + vagus nerve stimulation could provide insights into which modalities produce the strongest synergistic effects. This would allow for further refinement of personalized treatment protocols based on individual health needs and goals.
Additionally, more extensive biomarker analysis could help quantify the cellular-level changes induced by the Recharge Portal. Future studies should incorporate blood-based inflammatory markers (CRP, IL-6, NFKB), mitochondrial function tests, and advanced metabolic assessments to further elucidate the underlying mechanisms driving these improvements. Neurocognitive assessments, including memory, focus, and executive function tests, could also be employed to measure the effects of vagus nerve stimulation and curcumin supplementation on brain health.
The Recharge Portal presents a novel and time-efficient approach to optimizing metabolic function, autonomic regulation, and longevity-related biomarkers. This study provides compelling evidence that a single session can significantly enhance mitochondrial efficiency, autonomic nervous system balance, and fat oxidation while also reducing biological age markers. Future research should focus on long-term effects, comparative studies of individual therapy combinations, and expanded biomarker tracking to further validate and refine this innovative intervention.
Source
Epel, E. S. (2020). The geroscience agenda: Toxic stress, hormetic stress, and the rate of aging. Ageing Research Reviews, 63, 101167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101167



